Utilities is a set of quick calculation utilities to provide users with a means of estimating various parameters of interest about CEOS satellite missions. Utilities for repeating orbits and swath calculators are provided. Under the Repeating Orbit tab, users may estimate the Ground Track Interval, Period/Velocity, and Sun Synchronous Orbit. Under the Swath Calculator tab, users may estimate the Incidence to Pointing angle, Swath/FOV, Swath from Incidence and Swath/Off-nadir.
Utilities can be launched from the Tools menu in the title menu bar.
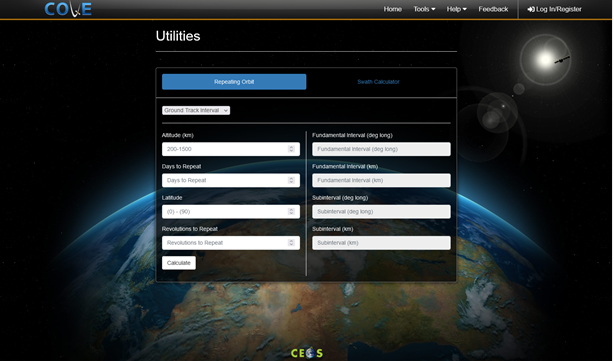
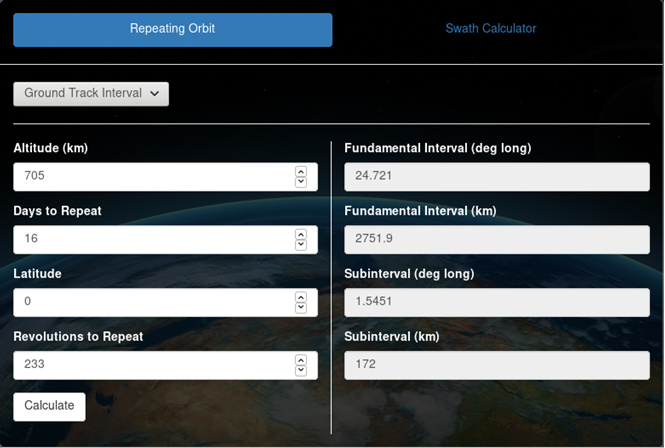
Ground track interval calculator
Ground track interval may be calculated by providing altitude or revolutions to repeat, days to repeat, and latitude, and clicking "Calculate". Fundamental interval and subinterval will be displayed in degrees longitude and kilometers. The following calculations are used:
-
Revolutions to repeat:
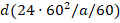 where
d is the days to repeat and a is the orbital period
where
d is the days to repeat and a is the orbital period
- Fundamental interval (in deg long): 360 / (revolutions to repeat / days to repeat)
- Subinterval (in deg long): fundamental interval / days to repeat
-
Convert fundamental interval/subinterval (deg long) to km:
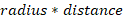 where
where
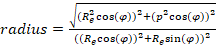 and
and
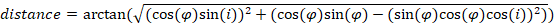
Re is the earth equatorial radius constant (6378.13649), p is a polar radius constant (6356.7523), φ is latitude,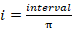
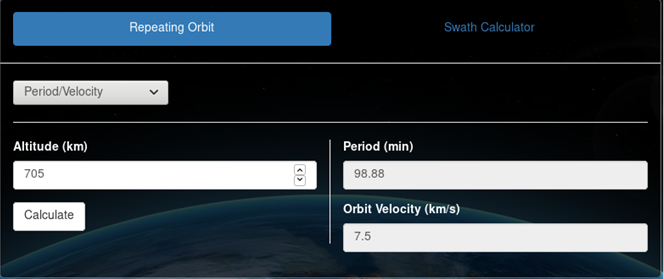
Period/Velocity calculator
Period/Velocity may be calculated by providing altitude and clicking "Calculate". Orbital period (min) and velocity (km/s) will be displayed. The following calculations are used:
-
Period:
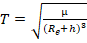 where
μ is the gravitational parameter (398600.4415), r is earth
equatorial radius constant (6378.13649), h is altitude
where
μ is the gravitational parameter (398600.4415), r is earth
equatorial radius constant (6378.13649), h is altitude
-
Velocity:
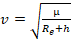 where
μ is the gravitational parameter (398600.4415), r is earth
equatorial radius constant (6378.13649), h is altitude
where
μ is the gravitational parameter (398600.4415), r is earth
equatorial radius constant (6378.13649), h is altitude
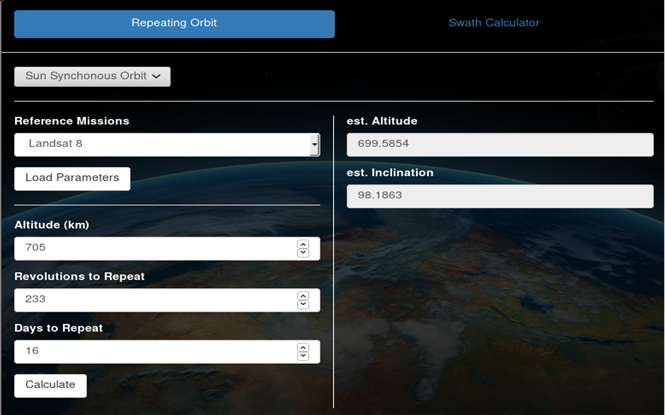
Sun Synchronous Orbit calculator
Sun Synchronous Orbit may be calculated by providing altitude and revolutions to repeat, days to repeat (optional), and clicking "Calculate". Days to repeat may be calculated from altitude and revolutions to repeat if not provided. Orbit parameters may also be loaded from select reference missions in COVE. The reference missions available are ALOS-2, Landsat 8, NPP, Sentinel-1A, Sentinel-1B. If users choose to use parameters from reference missions, click "Load Parameters" to retrieve mission parameters from COVE. Once the "Calculate" button is clicked, the estimated altitude and estimated inclination will be displayed. The following calculations are used:
-
Days to repeat:
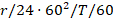 where
r is revolutions to repeat and T is the orbital period (using
period calculation above)
where
r is revolutions to repeat and T is the orbital period (using
period calculation above)
-
Estimated altitude:
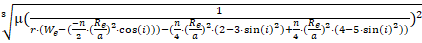 where
a is altitude, r is revolutions per day (revolutions to repeat /
days to repeat), i is inclination, μ is the gravitational
parameter (398600.4415),
where
a is altitude, r is revolutions per day (revolutions to repeat /
days to repeat), i is inclination, μ is the gravitational
parameter (398600.4415),
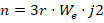 ,
,
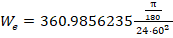 ,
and j2 is a zonal harmonic constant (0.001082626335439)
,
and j2 is a zonal harmonic constant (0.001082626335439)
-
Estimated inclination:
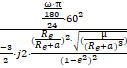 where
e is the earth equatorial radius constant (6378.13649), a is altitude,
j2 is a zonal harmonic constant (0.001082626335439), μ is the
gravitational parameter (398600.4415), e is eccentricity (value is 0), and
where
e is the earth equatorial radius constant (6378.13649), a is altitude,
j2 is a zonal harmonic constant (0.001082626335439), μ is the
gravitational parameter (398600.4415), e is eccentricity (value is 0), and
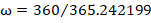
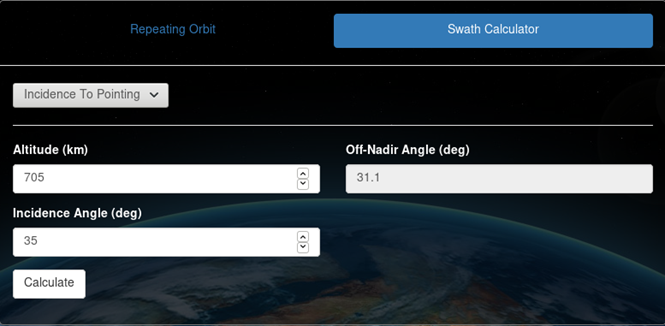
Incidence to Pointing calculator
Incidence to Pointing may be calculated by providing altitude (km), incidence angle (deg), and clicking "Calculate". Off-nadir pointing angle (deg) will be displayed. The following calculation is used:
-
Pointing angle:
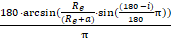 where
e is the earth equatorial radius constant (6378.13649), a is altitude, and
i is inclination
where
e is the earth equatorial radius constant (6378.13649), a is altitude, and
i is inclination
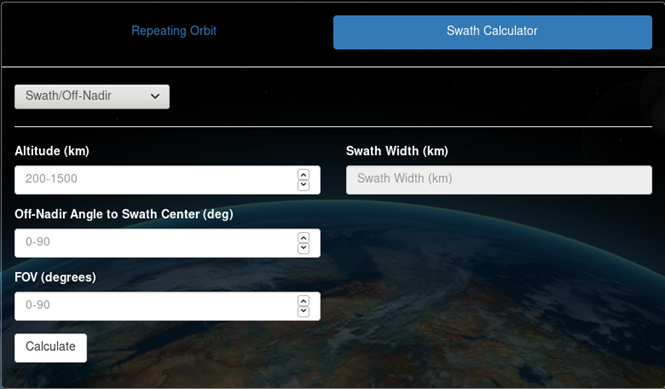
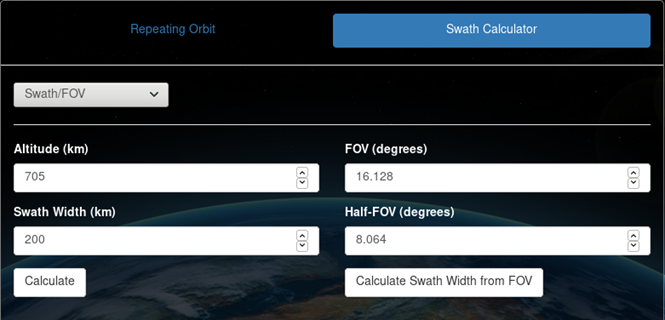
Swath/FOV calculator
Swath/FOV allows users to calculate ground swath width or field of view (FOV). Swath width may be calculated by providing altitude (km), half-FOV (deg), and clicking "Calculate Swath Width from FOV". FOV is calculated when half-FOV is entered. Swath width will be displayed. FOV/half-FOV may be calculated by providing altitude (km), swath width, and clicking "Calculate". FOV and half-FOV will be displayed.
-
Ground swath:
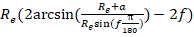 where
e is the earth equatorial radius constant (6378.13649), a is altitude,
f is half-FOV
where
e is the earth equatorial radius constant (6378.13649), a is altitude,
f is half-FOV
-
Half-FOV from swath:
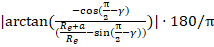 where
Re is the earth equatorial radius constant (6378.13649), a is altitude, and
where
Re is the earth equatorial radius constant (6378.13649), a is altitude, and
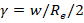 where
w is swath width
where
w is swath width
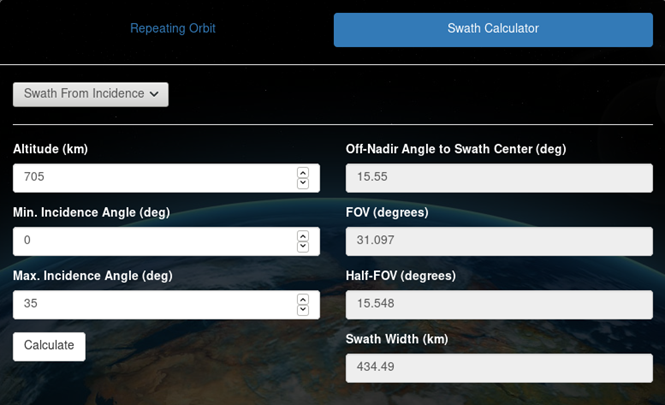
Swath from Incidence calculator
Swath from Incidence may be calculated by providing altitude (km), minimum and maximum incidence angles (deg), and clicking "Calculate". Off-nadir pointing angle from swath center (deg), FOV (deg), half-FOV (deg), and swath width (km) will be displayed. The following calculation is used:
-
Convert incidence angle to off-nadir angle:
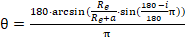 where
Re is the earth equatorial radius constant (6378.13649), a is altitude, and
i is the incidence angle (min or max).
where
Re is the earth equatorial radius constant (6378.13649), a is altitude, and
i is the incidence angle (min or max).
-
Off-nadir pointing angle from swath center:
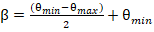 where
θmin is the minimum off-nadir angle and θmax is
the maximum off-nadir angle.
where
θmin is the minimum off-nadir angle and θmax is
the maximum off-nadir angle.
-
Half-FOV:
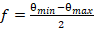 where θmin is the minimum off-nadir angle and θ
max is the maximum off-nadir angle. Full-FOV is f * 2.
where θmin is the minimum off-nadir angle and θ
max is the maximum off-nadir angle. Full-FOV is f * 2.
-
Swath width:
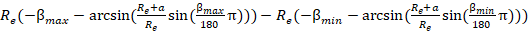 where Re is the earth equatorial radius constant (6378.13649), a is
altitude, βmin is β - f, and βmax is
β + f.
where Re is the earth equatorial radius constant (6378.13649), a is
altitude, βmin is β - f, and βmax is
β + f.
Swath from Off-nadir calculator
Swath from Off-nadir may be calculated by providing altitude (km), off-nadir pointing angle (deg), full FOV (deg), and clicking "Calculate". Swath width (km) will be displayed. The following calculation is used:
-
Swath width:
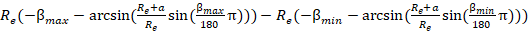 where Re is the earth equatorial radius constant (6378.13649), a is altitude,
βmin is β - f, and βmax is β + f.
where Re is the earth equatorial radius constant (6378.13649), a is altitude,
βmin is β - f, and βmax is β + f.